x inactivation|x inactivation in females : Tuguegarao Learn how imprinting and X inactivation regulate gene expression in mammals. Imprinting depends on parental origin and methylation, while X inactivation turns off one X . 10 de nov. de 2023 · The Connectivity Standards Alliance, best known for being behind the cross-vendor Matter Internet of Things (IoT) standard, is turning its focus to smart locks with Aliro — and has already signed up one of the largest lock makers around, ASSA ABLOY.
0 · x inactivation wikipedia
1 · x inactivation vs imprinting
2 · x inactivation in humans
3 · x inactivation in females
4 · x inactivation example
5 · x inactivation definition
6 · x inactivation and imprinting
7 · how does x inactivation work
Resultado da 4 de dez. de 2019 · Geisy fez a receita e Kid Bengala acompanhou tudo. O ator revelou que estava realizando um “sonho” ao comer a iguaria natalina feita por Geisy Arruda. No vídeo de temática natalina, Geisy e Kid usaram gorro de papai noel. O canal de Geisy Arruda não para de crescer no .
x inactivation*******Learn how X-inactivation prevents human females from having two active X chromosomes in each cell, and how it affects disorders of sex chromosome number. See examples of X-inactivation in cats, humans, and kangaroos. See more
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them fro. X-inactivation is a process that occurs in female mammals, including humans, to balance the expression of genes on the X chromosome. This book chapter explains how X-inactivation works, .
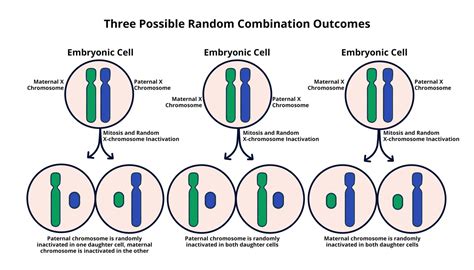
Learn how female mammals silence one of their two X chromosomes to balance gene expression and avoid dosage problems. Explore the roles of noncoding RNAs XIST and TSIX, and the difference between random .
x inactivation in femalesLearn how female mammals silence one of their two X chromosomes to balance gene expression and avoid dosage problems. Explore the roles of noncoding RNAs XIST and TSIX, and the difference between random .
Learn how imprinting and X inactivation regulate gene expression in mammals. Imprinting depends on parental origin and methylation, while X inactivation turns off one X . X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is the form of dosage compensation in mammalian female cells to balance X-linked gene expression levels of the two sexes. . X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is the form of dosage compensation in mammalian female cells to balance X-linked gene expression levels of the two sexes. Many diseases are related to XCI due to inactivation escape and skewing, and the symptoms and severity of these diseases also largely depend on the status of XCI. . A summary of the known elements and regions in the X-inactivation centre (Xic) thought to affect choice, counting and cis-inactivation during the initiation of X inactivation.(See Box 1 for more . In Xce heterozygotes, the X chromosome carrying the weaker of the two alleles is more likely to be inactivated. The degree of skewing can vary a lot, with cases of mean X inactivation patterns as profound as ∼25:75 in Xcec/Xcea hybrids [ 140 ]. Conversely, primary choice is presumably unbiased in Xce homozygotes.During X chromosome inactivation, another gene for noncoding RNA, Tsix, on Xi, is downregulated, but the Xist and Tsix genes need to interact with each other for X chromosome inactivation to take .
X-chromosome inactivation occurs randomly for one of the two X chromosomes in female cells during development. Inactivation occurs when RNA transcribed from the Xist gene on the X chromosome from which it is expressed spreads to coat the whole X chromosome. In the first issue of Epigenetics and Chromatin, . X inactivation represents a complex multi-layer epigenetic mechanism that profoundly modifies chromatin composition and structure of one X chromosome in females. The heterochromatic inactive X chromosome adopts a unique 3D bipartite structure and a location close to the nuclear periphery or the nucleolus. X-linked lncRNA loci and their .
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a mechanism for dosage compensation between males and females in mammal, during which one of the two X chromosomes of females is transcriptionally silenced. The XCI is mediated by the expression of XIST, an lncRNA from the future inactivated X chromosome (Xi). X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a key developmental process taking place in female mammals to compensate for the imbalance in the dosage of X-chromosomal genes between sexes. It is a formidable example of concerted gene regulation and a paradigm for epigenetic processes. Although XCI has been substantially deciphered in .
X-inactivation ensures that people with two X chromosomes have only one functional copy of the X chromosome in each cell. Because X-inactivation is random, normally, the X chromosome inherited from one parent is active in some cells, and the X chromosome inherited from the other parent is active in other cells. Some genes on the X .Despite this chromosome-wide silencing, a number of genes escape X inactivation: in women about 15% of X-linked genes are bi-allelically expressed and in mice, about 3%. Expression from the inactive X allele varies from a few percent of that from the active allele to near equal expression. While most genes have a stable inactivation pattern, a .
x inactivation X-inactivation is a well-established dosage compensation mechanism ensuring that X-chromosomal genes are expressed at comparable levels in males and females. Skewed X-inactivation is often .x inactivation x inactivation in females X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is an exemplar of epigenetic regulation that is set up as pluripotent cells differentiate. Once established, XCI is stably propagated, but can be reversed in vivo or by pluripotent reprogramming in vitro.Although reprogramming provides a useful model for inactive X (Xi) reactivation in mouse, the relative instability . X inactivation: a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated; Sex Chromosome Nondisjunction in Humans. Humans display dramatic deleterious effects with autosomal trisomies and monosomies. Therefore, it may seem counterintuitive that human females and males . Upon X inactivation, we and others showed that the inactive X-chromosome in the mouse undergoes massive structural rearrangement, yielding two chromosomal lobes or megadomains [13,68,73]. Within a megadomain loci interact with frequency, while there is very little interaction between chromosomal loci in opposite .X-inactivation is a random process that happens separately in individual cells during embryonic development. One cell might shut down the paternal X, while its next-door neighbor might shut down the maternal X instead. All the cells descended from each of these original cells will maintain the same pattern of X-inactivation.X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin .X inactivation only occurs in cells with multiple X chromosomes, which explains why almost all calico cats are female. X inactivation exists in two different forms: random and imprinted. In X-inactivation, an X chromosome is compacted (or, as my intro bio professor liked to say, "crumpled up into a ball"), to make a small, dense structure called a Barr body. Most of the genes on the Barr body are .
Paul Andersen explains how X inactivation works in mammals. This process was first described by Mary Lyon. Each cell in a female will have on activated and one inactivated X chromosome.

X inactivation turns off entire chromosomes, whereas imprinting turns off only specific genes. How do these processes work, and why do they often produce similar results? Lyonization (also called X-inactivation) refers to the normal phenomenon in which one of the two X chromosomes in every cell of a female individual is inactivated during embryonic development. Identical twins have the same DNA sequence, so how can one twin end up with a genetic disorder while the other twin does not? Robin Ball explains how the secret lies in X chromosome.
WEBPor favor, tente novamente. Letra da música Dono da Vida de Vanilda Bordieri - Maria saiu, saiu de manhã / Foi ver o mestre que estava ali / Tomou por surpresa quando não o avistou / Maria chorou e até perguntou o que fizeram com eleUma voz perguntou: Por que choras, mulher? / Pra onde levaram meu mestre daqui.
x inactivation|x inactivation in females